Lipomas represent approximately 0.15% of cerebellopontine angle tumors.1 Audiometric findings include unilateral or asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss with low speech recognition index (SRI).2 Imaging procedures, particularly nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), confirm the diagnosis.1–4 There is no image enhancement with gadolinium; in this scenario, special fat suppression sequences are particularly useful.3 In asymptomatic and mildly symptomatic patients, the treatment is expectant, and surgical approach should be reserved for cases of dizziness, as well as intense and clinically intractable trigeminal neuralgia and headache.3,4
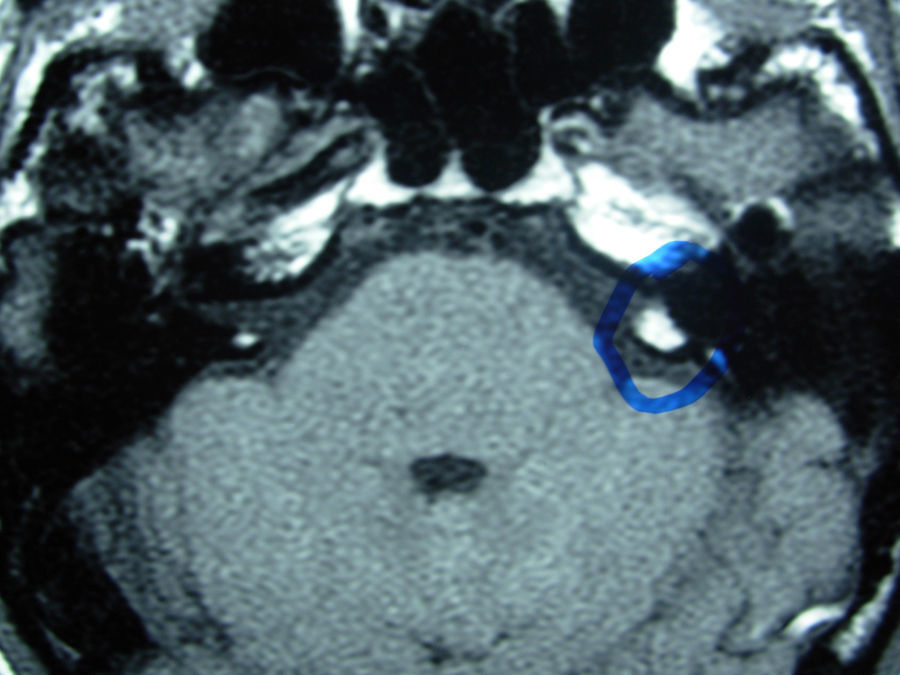
Case reportGPS, male, 30 years old, asymptomatic, referred after a change in periodic audiometry. The audiometry showed mild sensorineural hearing loss, with a flat curve in the left ear, and SRI was 100% in both ears. Brainstem evoked auditory potential (BEAP) revealed increase in left I–III interpeak interval. NMR of the internal auditory canals and cerebellopontine angles (CPA) showed a small extra-axial elongated image of approximately 0.8cm in greatest diameter in the upper portion of the left cerebellopontine angle cistern, that exhibited a fat-like signal intensity which disappeared with the use of fat-suppression technique. The Neurosurgery Service chose watchful waiting and audiometric follow-up. After one year, a repeat audiogram was performed with a second NMR; the size of the lesion (Fig. 1) was unchanged, and there was no worsening of hearing thresholds by pure tone audiometry.
DiscussionUnlike most cases described,1–4 this patient was asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. The audiometric findings (unilateral sensorineural hearing loss) are characteristic of retrocochlear lesions, except for the normal SRI.1 No references were found with regard of BEAP findings (I–III interval increase), which was compatible with retrocochlear lesions.
As in other retrococlear lesions, NMR is the diagnostic technique of choice to identify the critical features of a lipoma, the absence of image enhancement with gadolinium and the disappearance of the lesion with the use of fat-suppression techniques.3,4 Given the slow growth of the lesion, there is consensus in the literature that surgical treatment only is indicated for cases with clinically intractable symptoms.2,3
Final commentsCPA lipomas are rare lesions that behave like and should be treated similar to other tumors that occur in the same region. Our example of an asymptomatic case is unusual.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Figueiredo RR, de Azevedo AA, Figueiredo JA, Penido NO. Cerebellopontine angle lipoma in asymptomatic patients: case report. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;82:741–2.